This is not the first time the gaming industry has been targeted by attackers who compromise game developers, insert backdoors into a game’s build environment, and then have their malware distributed as legitimate software. In April 2013, Kaspersky Lab reported that a popular game was altered to include a backdoor in 2011. That attack was attributed to perpetrators Kaspersky called the Winnti Group.
Yet again, new supply-chain attacks recently caught the attention of ESET Researchers. This time, two games and one gaming platform application were compromised to include a backdoor. Given that these attacks were mostly targeted against Asia and the gaming industry, it shouldn’t be surprising they are the work of the group described in Kaspersky’s “Winnti – More than just a game”.
Three Cases, Same Backdoor
Although the malware uses different configurations in each case, the three affected software products included the same backdoor code and were launched using the same mechanism. While two of the compromised products no longer include the backdoor, one of the affected developers is still distributing the trojanized version: ironically, the game is named Infestation, and is produced by Thai developer Electronics Extreme. We have tried informing them several times, through various channels, since early February, but without apparent success.
Let’s look at how the malicious payload is embedded and then look into the details of the backdoor itself.
Embedding the payload
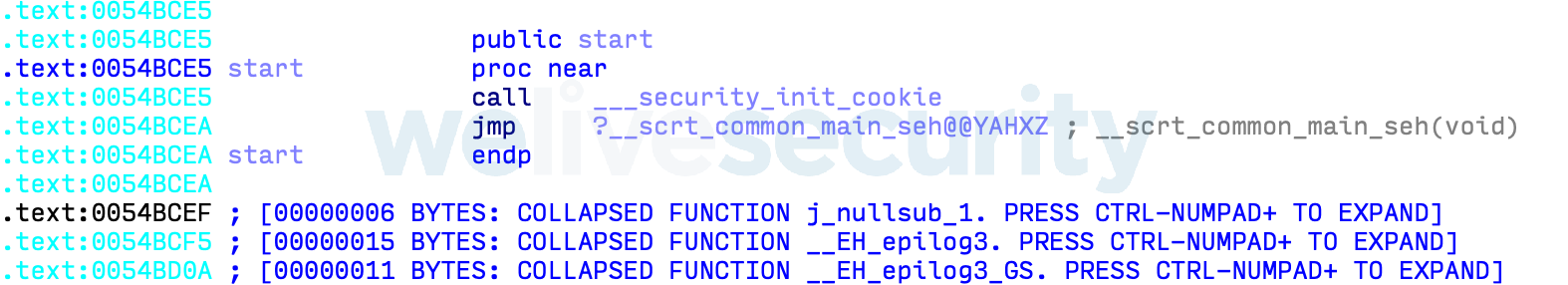
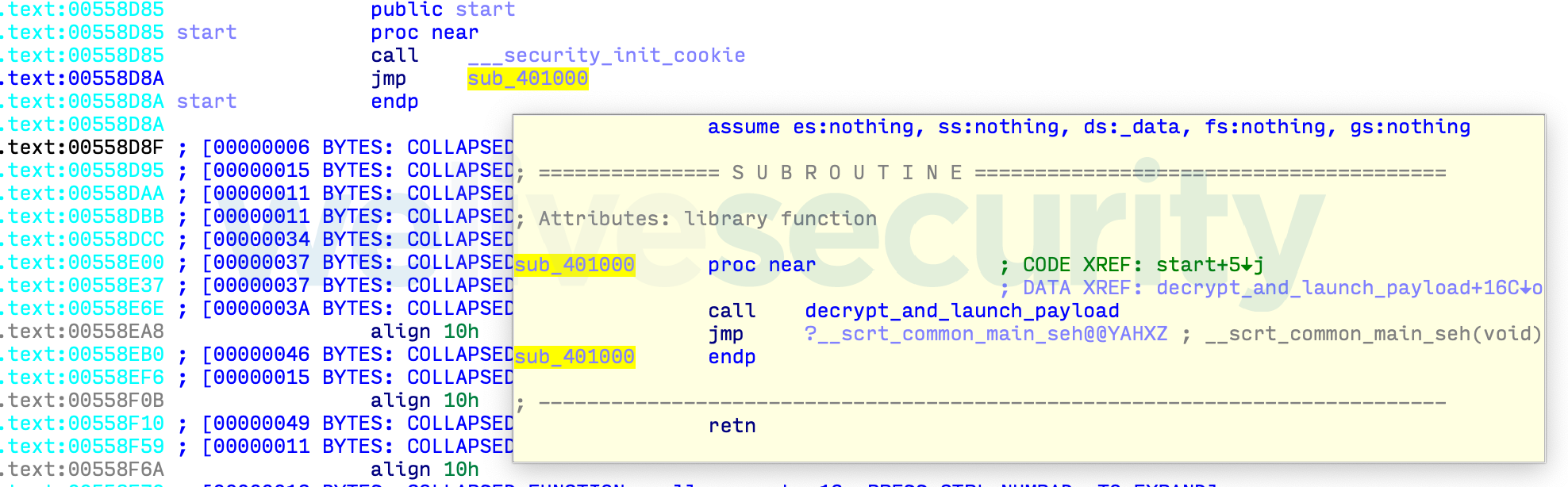
The payload code is started very early during the execution of the backdoored executable file. Right after the PE entry point, the standard call to the C Runtime initialization (__scrt_common_main_seh in Figure 1) is hooked to launch the malicious payload before everything else (Figure 2). This may suggest that the malefactor changed a build configuration rather than the source code itself.
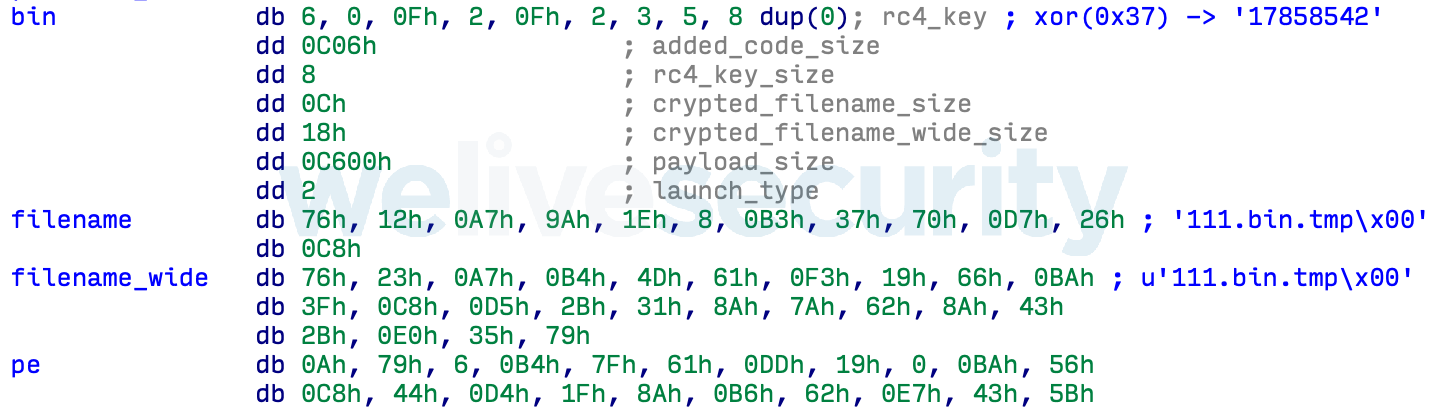
The code added to the executable decrypts and launches the backdoor in-memory before resuming normal execution of the C Runtime initialization code and all the subsequent code of the host application. The embedded payload data has a specific structure, seen in Figure 3, that is parsed by the added unpacking code.
It includes an RC4 key (which is XORed with 0x37) that is used to decrypt a filename and the embedded DLL file.
The malicious payload
The actual malicious payload is quite small and only contains about 17 KB of code and data.
Configuration
Illustrated in Figure 4, the configuration data is simply a whitespace-separated list of strings.
The configuration consists of four fields:
- C&C server URL.
- Variable (t) used to determine the time to sleep in milliseconds before continuing the execution. Wait time is chosen randomly in the range 2/3 t to 5/3 t.
- A string identifying a campaign.
- A semicolon-separated list of executable filenames. If any of them are running, the backdoor stops its execution.
ESET researchers have identified five versions of the payload:
| Truncated SHA-1 | PE Compile time (UTC) | C&C server URL |
|---|---|---|
a045939f |
2018-07-11 15:45:57 | https://bugcheck.xigncodeservice[.]com/Common/Lib/Common_bsod.php |
a260dcf1 |
2018-07-11 15:45:57 | https://bugcheck.xigncodeservice[.]com/Common/Lib/Common_Include.php |
dde82093 |
2018-07-11 15:45:57 | https://bugcheck.xigncodeservice[.]com/Common/Lib/common.php |
44260a1d |
2018-08-15 10:59:09 | https://dump.gxxservice[.]com/common/up/up_base.php |
8272c1f4 |
2018-11-01 13:16:24 | https://nw.infestexe[.]com/version/last.php |
In the first three variants, the code was not recompiled, but the configuration data was edited in the DLL file itself. The rest of the content is a byte for byte copy.
C&C infrastructure
Domain names were carefully chosen to look like they are related to the game or application publisher. The apex domain was set to redirect to a relevant legitimate site using the Namecheap redirection service, while the subdomain points to the malicious C&C server.
| Domain name | Registration date | Redirection target |
|---|---|---|
| xigncodeservice.com | 2018-07-10 09:18:17 | https://namu.wiki/[w]/XIGNCODE |
| gxxservice.com | 2018-08-14 13:53:41 | None or unknown |
| infestexe.com | 2018-11-07 08:46:44 | https://www.facebook.com/infest.[in].[th] |
| Subdomain name | IP addresses | Provider |
|---|---|---|
| bugcheck.xigncodeservice.com | 167.99.106[.]49, 178.128.180[.]206 | DigitalOcean |
| dump.gxxservice.com | 142.93.204[.]230 | DigitalOcean |
| nw.infestexe.com | 138.68.14[.]195 | DigitalOcean |
At the time of writing, none of the domains resolve and the C&C servers are not responding.
Reconnaissance report
A bot identifier is generated from the machine’s MAC address. The backdoor reports information about the machine such as the user name, computer name, Windows version and system language to the C&C server and awaits commands. The data is XOR encrypted with the key “*&b0i0rong2Y7un1” and base64-encoded. The data received from the C&C server is encrypted using the same key.
Commands
This simple backdoor has only four commands that can be used by the attacker:
- DownUrlFile
- DownRunUrlFile
- RunUrlBinInMem
- UnInstall
The commands are pretty much self-explanatory. They allow the attacker to run additional executables from a given URL.
The last one is perhaps less obvious. The UnInstall command doesn’t remove the malware from the system. After all, it is embedded inside a legitimate executable that still needs to run. Rather than removing anything, it disables the malicious code by setting the following registry value to 1:
- HKCU\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ImageFlag
When the payload is started, the registry value is queried and execution is aborted if set. Perhaps the attackers are trying to reduce the load from their C&C servers by avoiding callbacks from uninteresting victims.
Second stage
Based on ESET telemetry, one of the second stage payload delivered to victims is Win64/Winnti.BN. As far as we can tell, its dropper was downloaded over HTTPS from api.goallbandungtravel[.]com. We have seen it installed as a Windows service and as a DLL in C:\Windows\System32 using the following file names:
- cscsrv.dll
- dwmsvc.dll
- iassrv.dll
- mprsvc.dll
- nlasrv.dll
- powfsvc.dll
- racsvc.dll
- slcsvc.dll
- snmpsvc.dll
- sspisvc.dll
The samples we have analyzed were actually quite large, each of them about 60 MB. This is, however, only for appearance because the real size or the PE file is between 63 KB and 72 KB, depending on the version. The malware files simply have lots of clean files appended to them. This is probably done by the component that drops and installs this malicious service.
Once the service runs, it appends the extension .mui to its DLL path, reads that file and decrypts it using RC5. The decrypted MUI file contains position-independent code at offset 0. The RC5 key is derived from the hard drive serial number and the string “f@Ukd!rCto R$.” — we were not able to obtain any MUI files nor the code that installs them in the first place. Thus, we do not know the exact purpose of this malicious service.
Recent versions of the malware include an “auto-update” mechanism, using C&C server http://checkin.travelsanignacio[.]com. That C&C server served the latest version of the MUI files encrypted with a static RC5 key. The C&C server was not responding during our analysis.
Targets
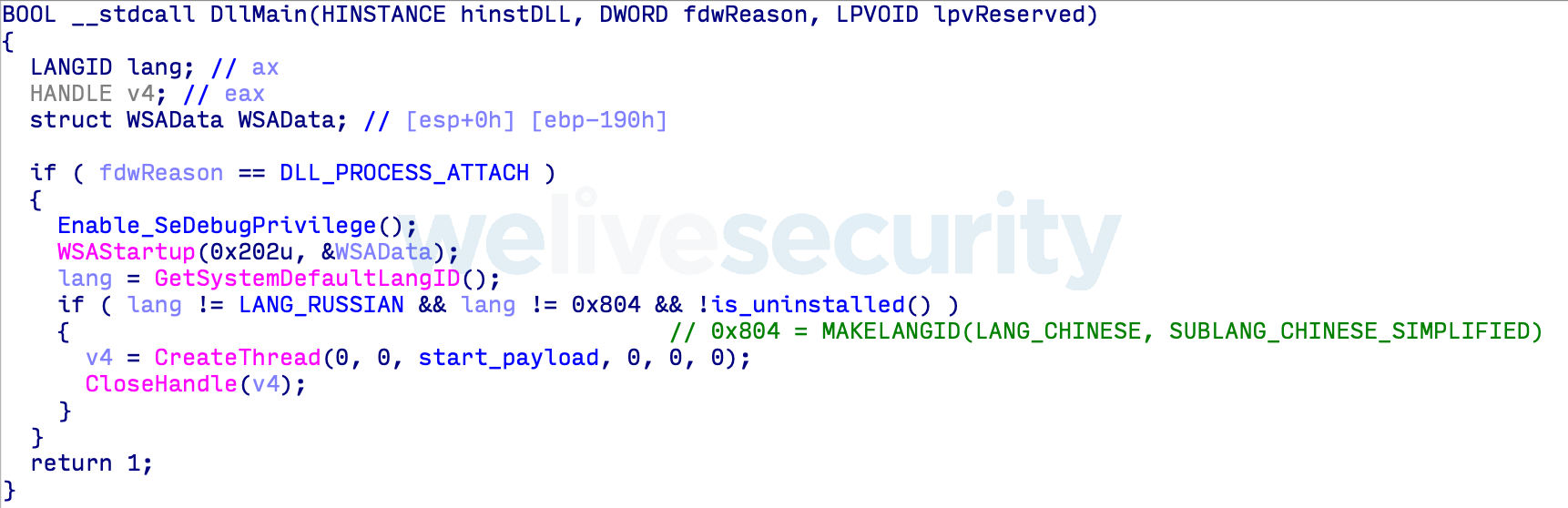
Let’s start with who is not targeted. Early in the payload, the malware checks to see if the system language is Russian or Chinese (Figure 5). In either case, the malware stops running. There is no way around this: the attackers are simply not interested in computers configured with those languages.
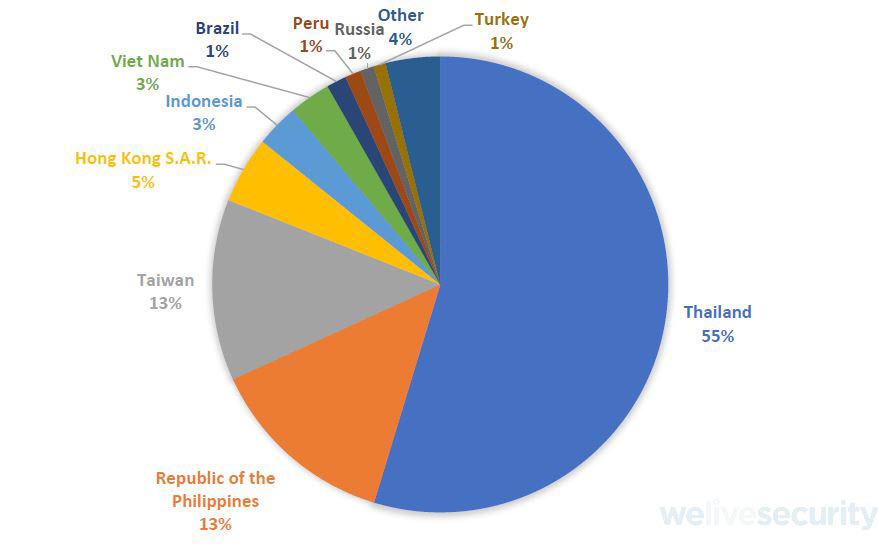
Distribution statistics
ESET telemetry shows victims are mostly located in Asia, with Thailand having the largest part of the pie. Given the popularity of the compromised application that is still being distributed by its developer, it wouldn’t be surprising if the number of victims is in the tens or hundreds of thousands.
Conclusion
Supply-chain attacks are hard to detect from the consumer perspective. It is impossible to start analyzing every piece of software we run, especially with all the regular updates we are encouraged or required to install. So, we put our trust in software vendors that the files they distribute don’t include malware. Perhaps that’s the reason multiple groups target software developers: compromising the vendor results in a botnet as popular as the software that is hacked. However, there is a downside of using such a technique: once the scheme is uncovered, the attacker loses control and computers can be cleaned through regular updates.
We do not know the motives of the attackers at this point. Is it simply financial gain? Are there any reasons why the three affected products are from Asian developers and for the Asian market? Do these attackers use a botnet as part of a larger espionage operation?
ESET products detect this threat as Win32/HackedApp.Winnti.A, Win32/HackedApp.Winnti.B, the payload as Win32/Winnti.AG, and the second stage as Win64/Winnti.BN.
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
Compromised file samples (Win32/HackedApp.Winnti.A and B)
| SHA-1 | Compile Time (UTC) | RC4 key | Payload SHA-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
474b1c81de1eafe93602c297d701418658cf6feb |
Mon Jul 16 07:37:14 2018 | 207792894 |
a045939f |
47dd117fb07cd06c8c6faa2a085e0d484703f5fd |
Wed Jul 25 06:44:09 2018 | 207792894 |
a045939f |
54b161d446789c6096362ab1649edbddaf7145be |
Tue Sep 4 08:02:38 2018 | 165122939 |
a260dcf1 |
67111518fe2982726064ada5b23fd91d1eb3d48e |
Wed Sep 19 09:51:44 2018 | 17858542 |
dde82093 |
0f31ed081ccc18816ca1e3c87fe488c9b360d02f |
Fri Sep 28 05:32:30 2018 | 17858542 |
dde82093 |
5e2b7b929471ac3ba22a1dfa851fac1044a698dc |
Tue Oct 16 05:09:15 2018 | 17858542 |
dde82093 |
132e699e837698ef090e3f5ad12400df1b1e98fa |
Thu Oct 18 02:53:03 2018 | 17858542 |
dde82093 |
d4eaf47253fe59f11a06517bb9e2d5e8b785abf8 |
Thu Nov 1 07:00:55 2018 | 17858542 |
dde82093 |
7cf41b1acfb05064518a2ad9e4c16fde9185cd4b |
Tue Nov 13 10:12:58 2018 | 1729131071 |
8272c1f4 |
7f73def251fcc34cbd6f5ac61822913479124a2a |
Wed Nov 14 03:50:18 2018 | 19317120 |
44260a1d |
dac0bd8972f23c9b5f7f8f06c5d629eac7926269 |
Tue Nov 27 03:05:16 2018 | 1729131071 |
8272c1f4 |
Some hashes were redacted per request from one of the vendor. If for a particular reason you need them, reach out to us at threatintel@eset.com.
Payload Samples (Win32/Winnti.AG)
| SHA-1 | C&C server URL |
|---|---|
a045939f53c5ad2c0f7368b082aa7b0bd7b116da |
https://bugcheck.xigncodeservice[.]com/Common/Lib/Common_bsod.php |
a260dcf193e747cee49ae83568eea6c04bf93cb3 |
https://bugcheck.xigncodeservice[.]com/Common/Lib/Common_Include.php |
dde82093decde6371eb852a5e9a1aa4acf3b56ba |
https://bugcheck.xigncodeservice[.]com/Common/Lib/common.php |
8272c1f41f7c223316c0d78bd3bd5744e25c2e9f |
https://nw.infestexe[.]com/version/last.php |
44260a1dfd92922a621124640015160e621f32d5 |
https://dump.gxxservice[.]com/common/up/up_base.php |
Second stage samples (Win64/Winnti.BN)
Dropper delivered by api.goallbandungtravel[.]com.
| SHA-1 | Compile Time (UTC) | C&C server URL prefix |
|---|---|---|
4256fa6f6a39add6a1fa10ef1497a74088f12be0 |
2018-07-25 10:13:41 | None |
bb4ab0d8d05a3404f1f53f152ebd79f4ba4d4d81 |
2018-10-10 09:57:31 | http://checkin.travelsanignacio[.]com |
MITRE ATT&CK matrix
| ID | Description |
|---|---|
| T1195 | Supply Chain Compromise |
| T1050 | New Service |
| T1022 | Data Encrypted |
| T1079 | Multilayer Encryption |
| T1032 | Standard Cryptographic Protocol (RC4, RC5) |
| T1043 | Commonly Used Port (80,443) |
| T1009 | Binary Padding |