This article sheds light on the current ecosystem of the Sathurbot backdoor trojan, in particular exposing its use of torrents as a delivery medium and its distributed brute-forcing of weak WordPress administrator accounts.
The torrent leecher
Looking to download a movie or software without paying for it? There might be associated risks. It just might happen that your favorite search engine returns links to torrents on sites that normally have nothing to do with file sharing. They may, however, run WordPress and have simply been compromised.
Some examples of search results:
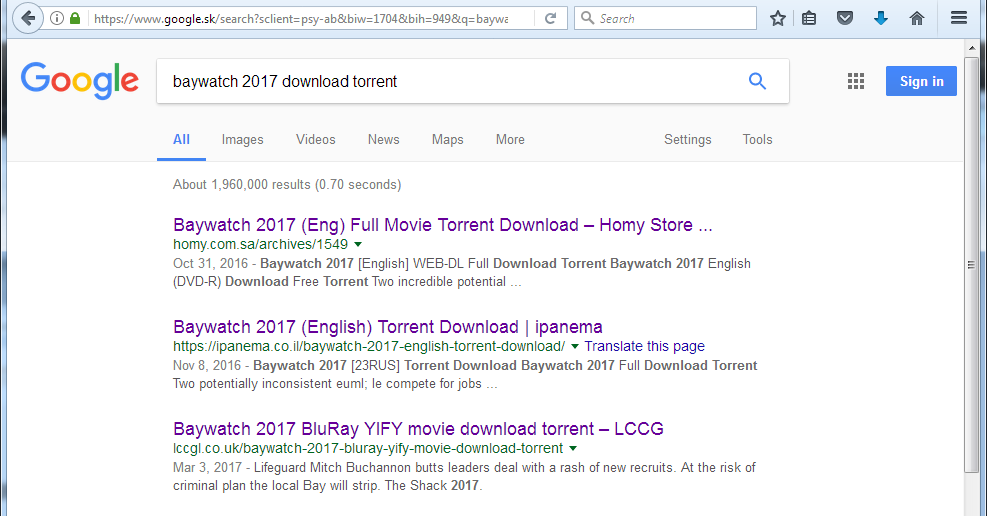
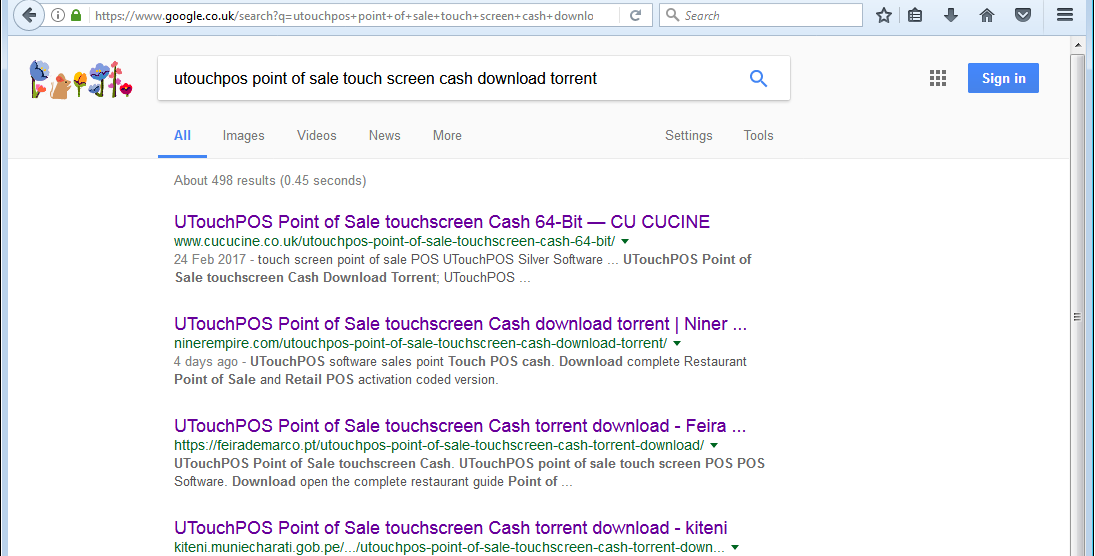
Clicking on some of those links returns the pages below (notice how some even use HTTPS):
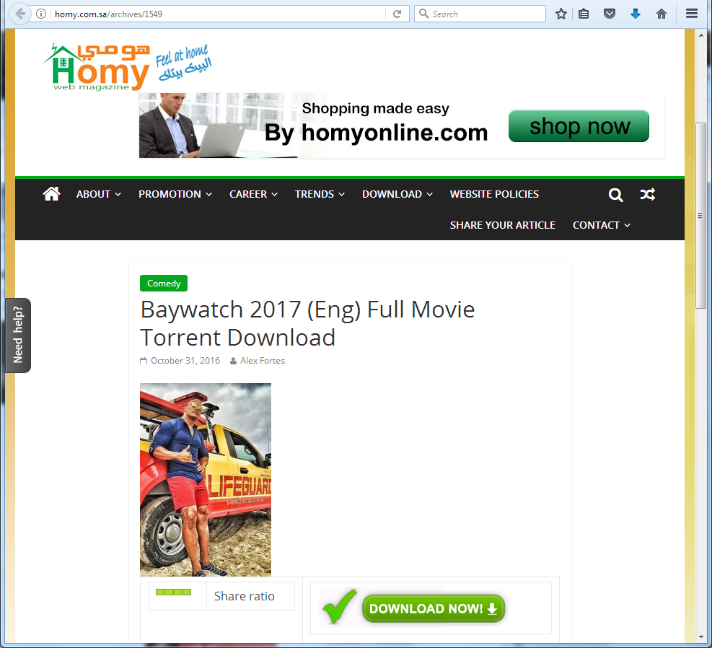

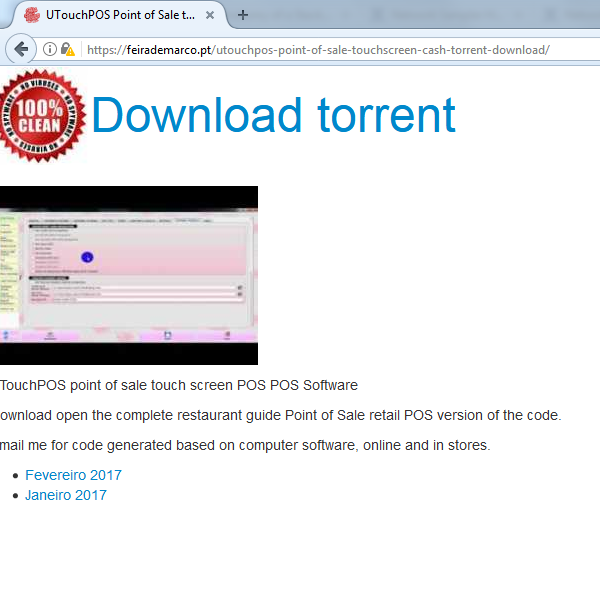
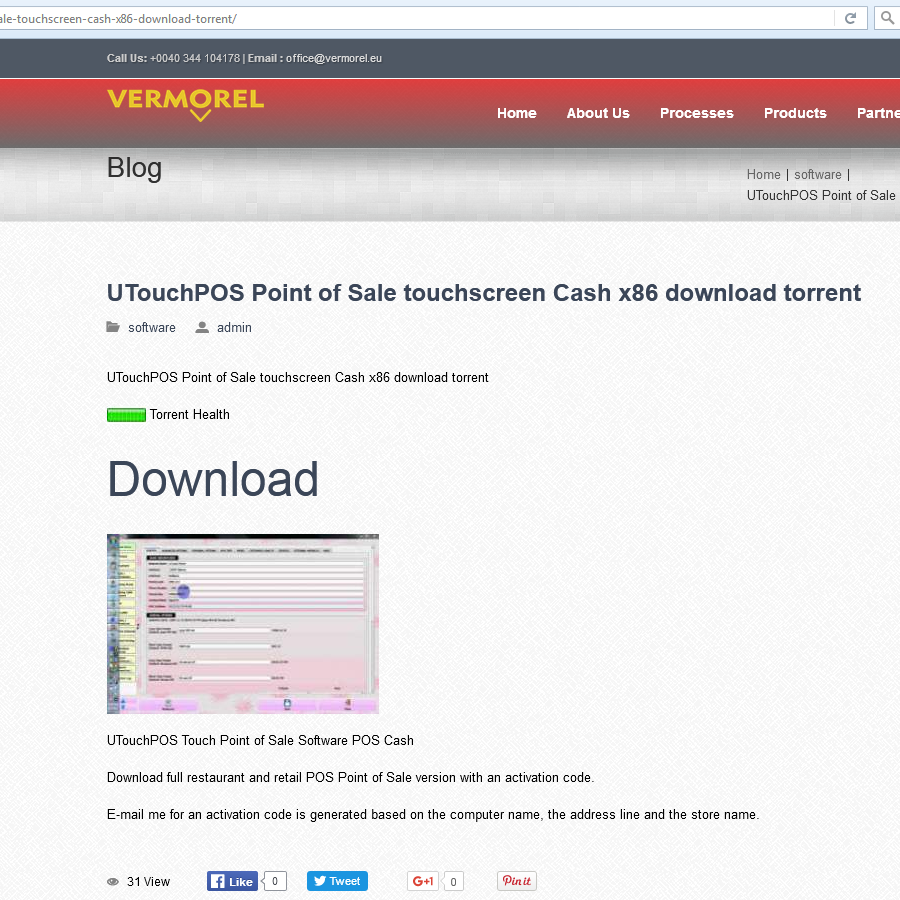
The movie subpages all lead to the same torrent file; while all the software subpages lead to another torrent file. When you begin torrenting in your favorite torrent client, you will find the file is well-seeded and thus appears legitimate. If you download the movie torrent, its content will be a file with a video extension accompanied by an apparent codec pack installer, and an explanatory text file. The software torrent contains an apparent installer executable and a small text file. The objective of both is to entice get the victim to run the executable which loads the Sathurbot DLL.
After you start the executable, you are presented with a message like this:
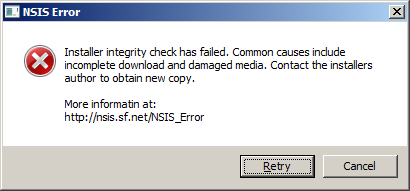
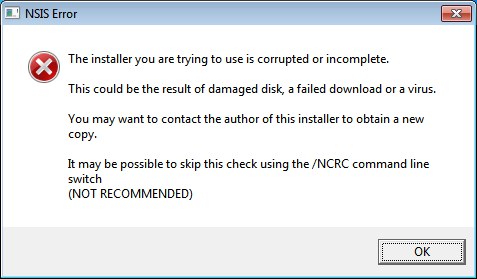
While you ponder your options, bad things start to happen in the background. You have just become a bot in the Sathurbot network.
Backdoor and downloader
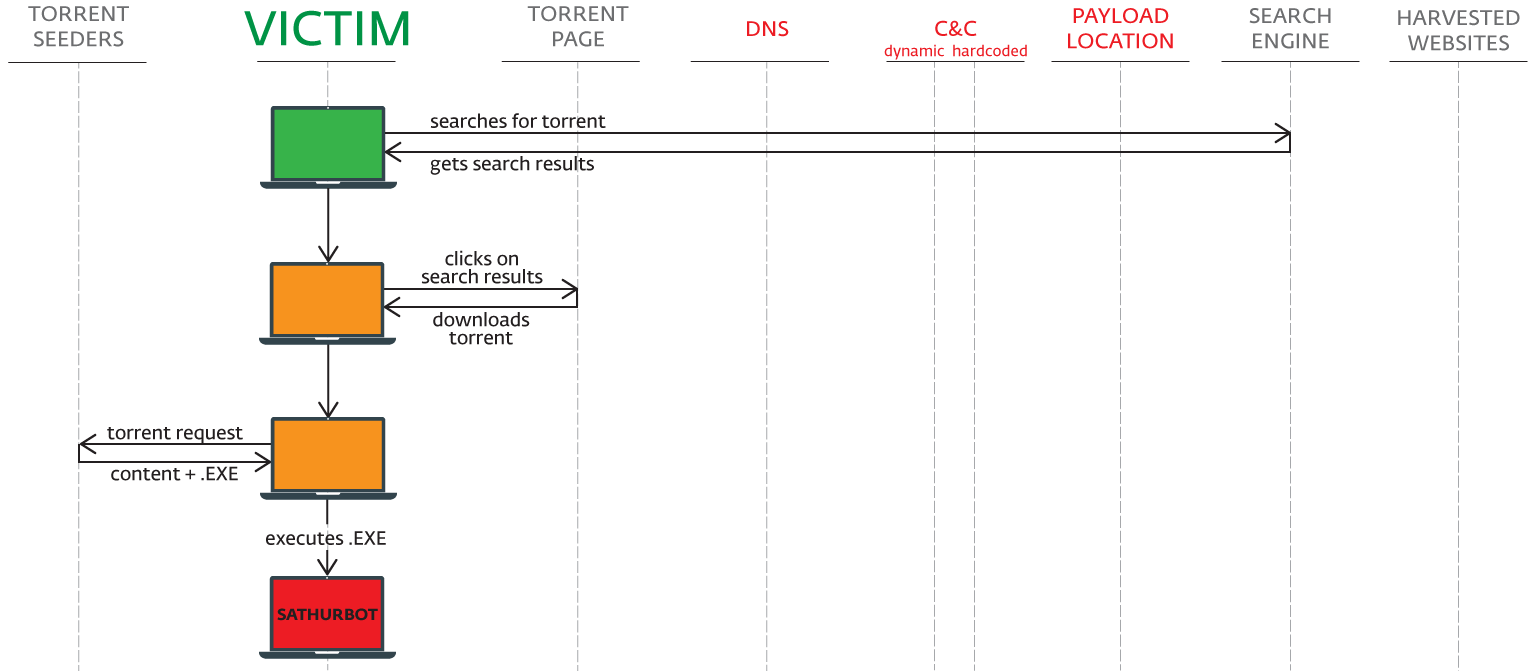
On startup, Sathurbot retrieves its C&C with a query to DNS. The response comes as a DNS TXT record. Its hex string value is decrypted and used as the C&C domain name for status reporting, task retrieval and to get links to other malware downloads.
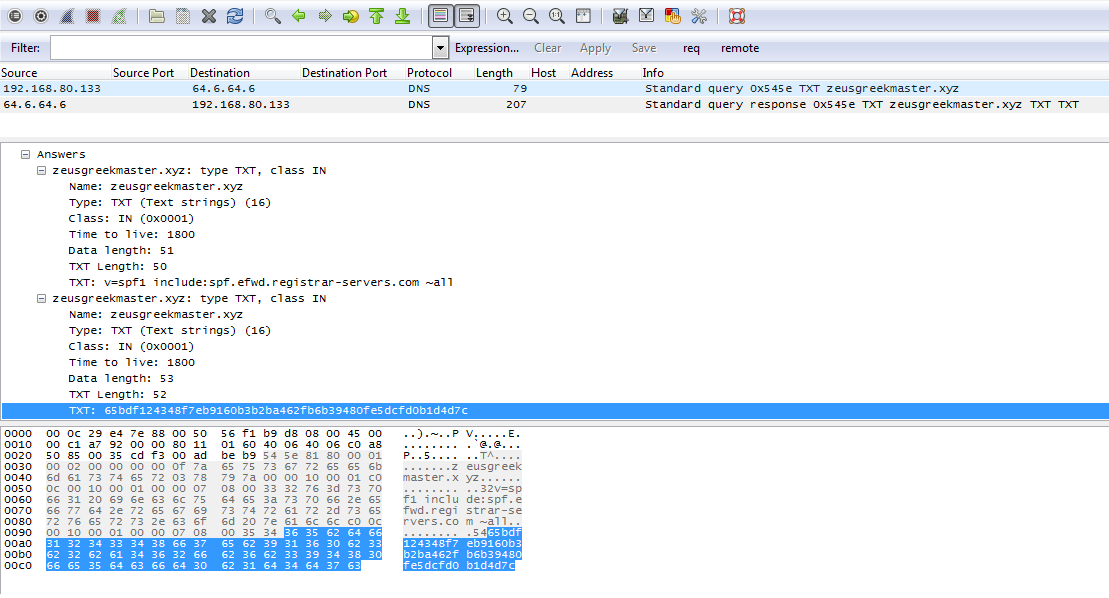
Sathurbot can update itself and download and start other executables. We have seen variations of Boaxxe, Kovter and Fleercivet, but that is not necessarily an exhaustive list.
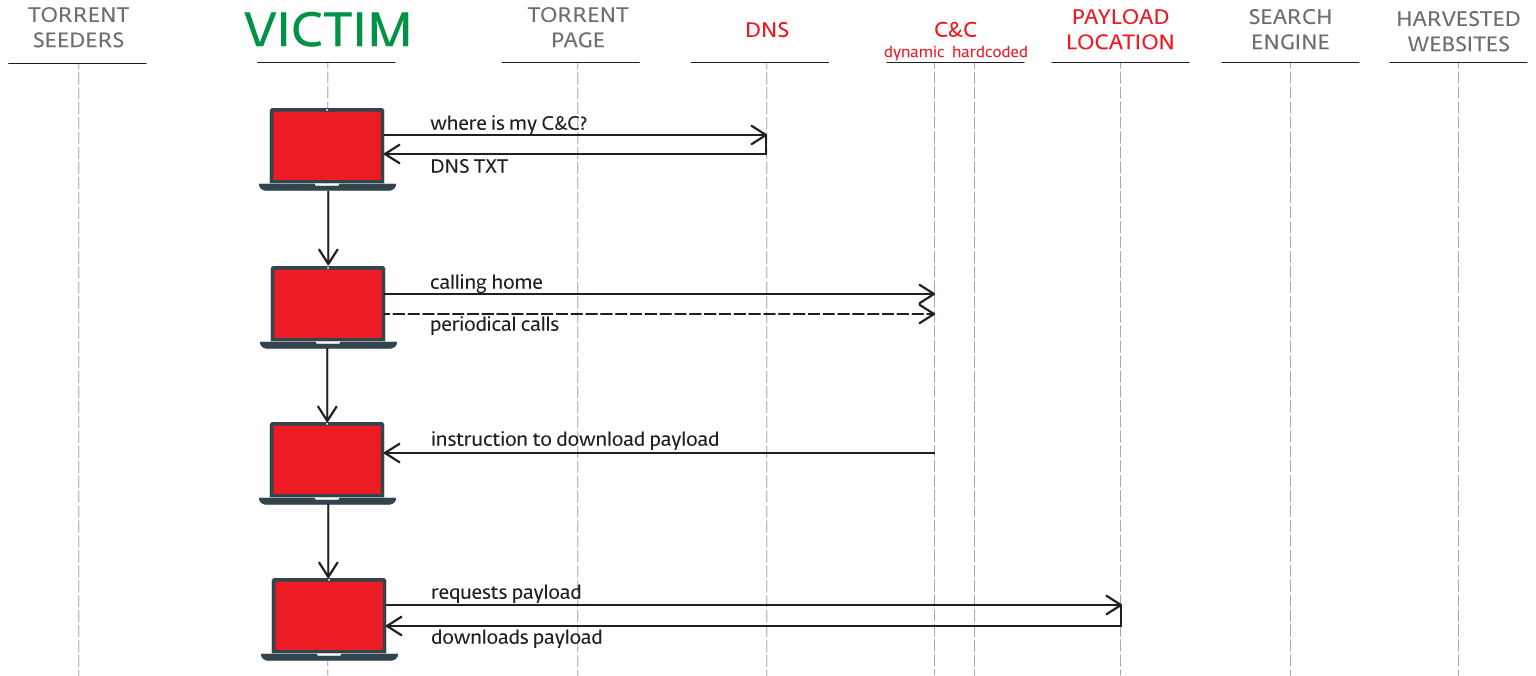
The Sathurbot then reports its successful installation along with a listening port to the C&C. Periodically, it reports to the C&C that it is alive and well, waiting for additional tasks.
Web crawler
Sathurbot comes with some 5,000 plus basic generic words. These are randomly combined to form a 2-4 word phrase combination used as a query string via the Google, Bing and Yandex search engines.
From the webpages at each of those search result URLs, a random 2-4 word long text chunk is selected (this time it might be more meaningful as it is from real text) and used for the next round of search queries.
Finally, the second set of search results (up to first three pages) are harvested for domain names.
The extracted domain names are all subsequently probed for being created by the WordPress framework. The trick here is to check the response for the URL http://[domain_name]/wp-login.php.
Afterward the root index page of the domain is fetched and probed for the presence of other frameworks. Namely, they are also interested in: Drupal, Joomla, PHP-NUKE, phpFox, and DedeCMS.
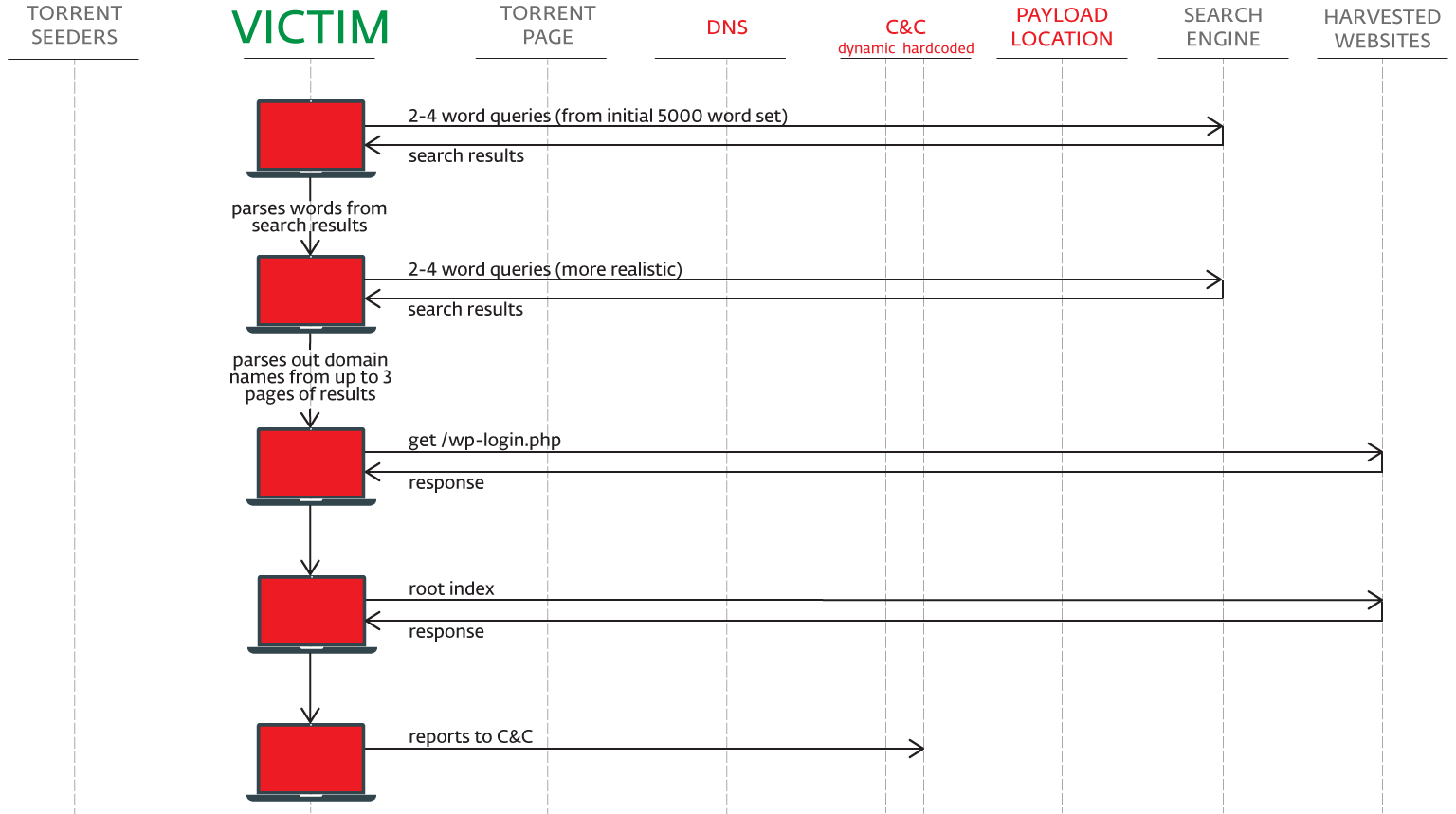
Upon startup, or at certain time intervals, the harvested domains are sent to the C&C (a different domain is used than the one for the backdoor – a hardcoded one).
Distributed WordPress password attack
The client is now ready to get a list of domain access credentials (formatted as login:password@domain) to probe for passwords. Different bots in Sathurbot’s botnet try different login credentials for the same site. Every bot only attempts a single login per site and moves on. This design helps ensure that the bot doesn’t get its IP address blacklisted from any targeted site and can revisit it in the future.
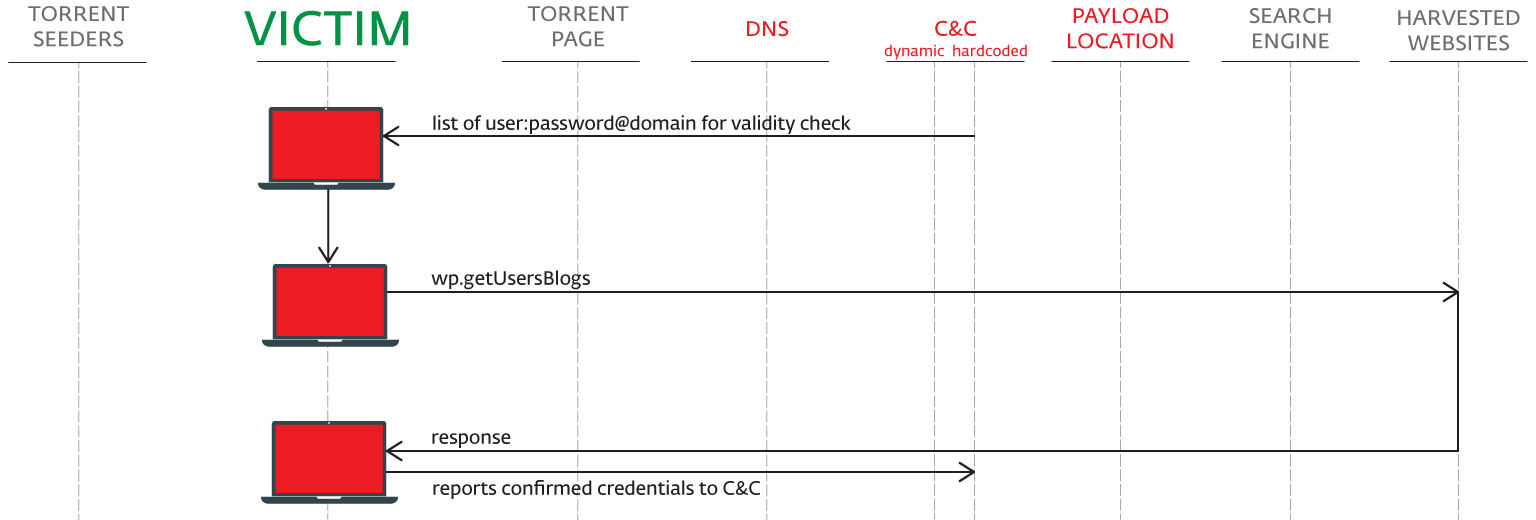
During our testing, lists of 10,000 items to probe were returned by the C&C.
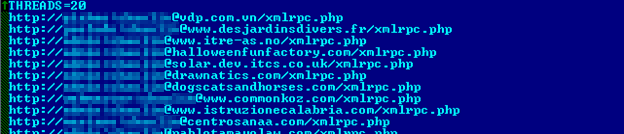
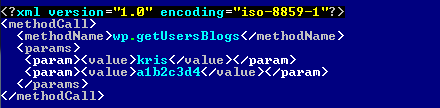
For the attack itself, the XML-RPC API of WordPress is used. Particularly the wp.getUsersBlogs API is abused. A typical request looks like:
The sequence of probing a number of domain credentials is illustrated in the following figure:
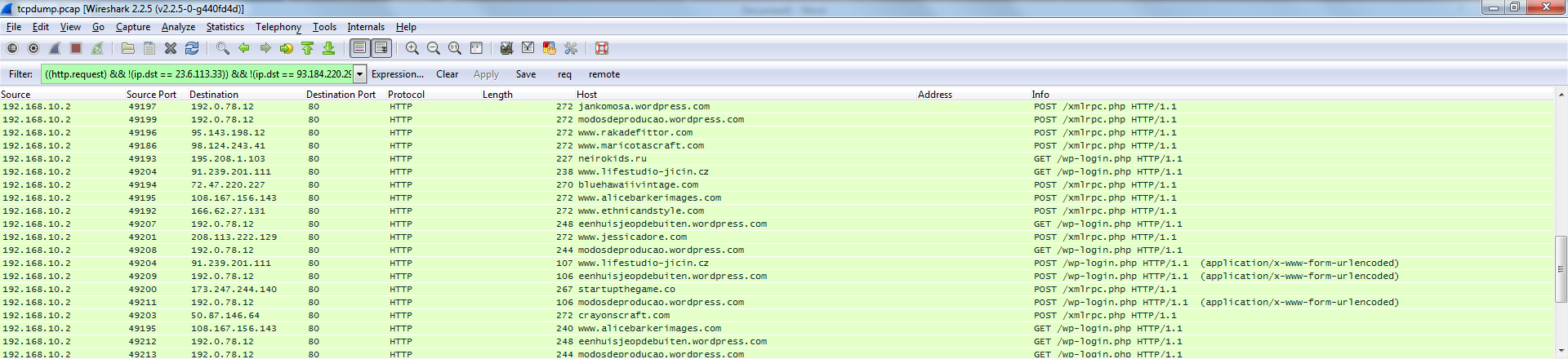
The response is evaluated and results posted to the C&C.
Torrent client – seeder
The bot has the libtorrent library integrated and one of the tasks is to become a seeder – a binary file is downloaded, torrent created and seeded.
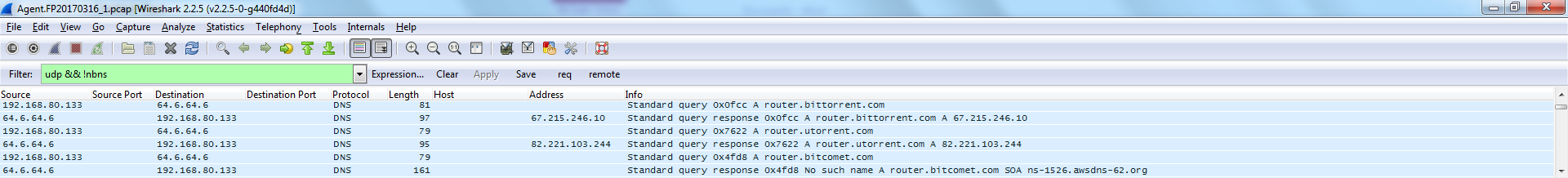
The BitTorrent bootstrap
That completes the cycle from a leecher to an involuntary seeder:
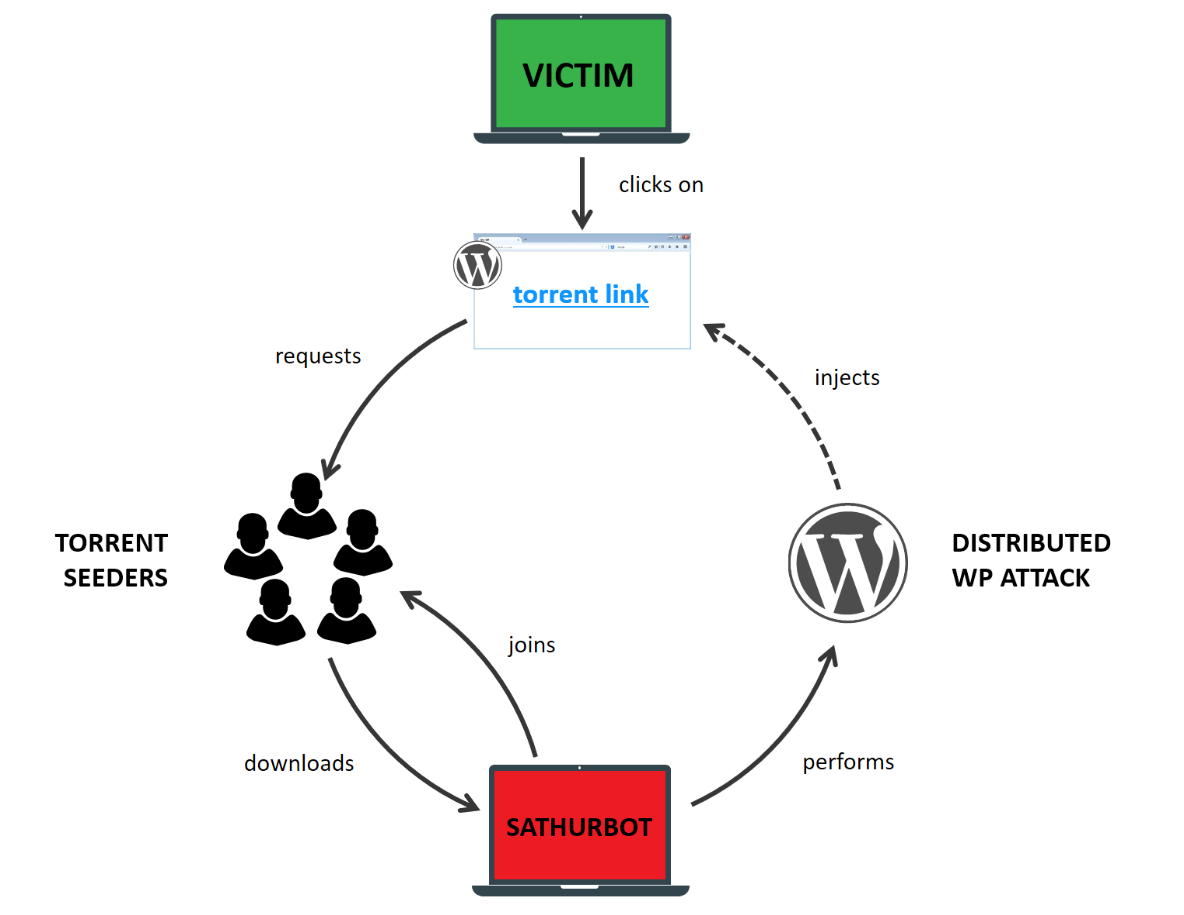
Note: Not every bot in the network is performing all the functions, some are just web crawlers, some just attack the XML-RPC API, and some do both. Also, not every bot seems to be seeding a torrent.
Impact
The above-mentioned attempts on /wp-login.php from a multitude of users, even to websites that do not host WordPress, is the direct impact of Sathurbot. Many web admins observe this and wonder why it is happening. In addition, WordPress sites can see the potential attacks on wp.getUsersBlogs in their logs.
Through examination of logs, system artifacts and files, the botnet consists of over 20,000 infected computers and has been active since at least June 2016.
Occasionally, we have seen torrent links being sent by email as well.
Detection
Web Admins – Check for unknown subpages and/or directories on the server. If they contain any references to torrent download offers, check logs for attacks and possible backdoors.
Users – Run Wireshark with the filter http.request with no web browser open to see too many requests like GET /wp-login.php and/or POST /xmlrpc.php. Alternatively, check for files or registry entries listed in the IoC section, below.
ESET users are protected from this threat on multiple levels.
Removal
Web Admins – Change passwords, remove subpages not belonging to site, optionally wipe and restore the site from a backup.
Users – Using a third-party file manager find the suspect .DLL (note that the files and directories have the hidden attribute set), open Process Explorer or Task Manager, kill explorer.exe and/or rundll32.exe, delete (quarantine) the affected .DLL, reboot.
Note: this will remove Sathurbot only, and not any other malware it may have also downloaded.
Alternatively, consider a comprehensive anti-malware product, or at least an online scanner.
Prevention
Web Admins - Should the normal functioning of the website not require the XML-RPC API, you are advised to disable it and use complex passwords.
Users – Avoid both running executables downloaded from sources other than those of respected developers, and downloading files from sites not designed primarily as file-sharing sites.
IoCs
Currently, we have observed Sathurbot installing to:
\ProgramData\Microsoft\Performance\Monitor\PerformanceMonitor.dll
\ProgramData\Microsoft\Performance\TheftProtection\TheftProtection.dll
\ProgramData\Microsoft\Performance\Monitor\SecurityHelper.dll
\Users\*****\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Protect\protecthost.dll
Runs in the context of rundll32.exe or explorer.exe process and locks files and registry keys from editing. It is present in both x32 and x64 bit versions in the installer.
Subfolders to the above (contain the seeded files by torrent)
\SecurityCache\cache\resume\
\SecurityCache\cache\rules\
\SecurityCache\data\
\SecurityCache\zepplauncher.mif - contains the DHT nodes
\temp\
%appdata%\SYSHashTable\ - contains folders representing the hashes of visited domains
%appdata%\SYSHashTable\SyshashInfo.db - collection of interesting domains found incl. framework info
Samples (SHA-1)
Installers:
2D9AFB96EAFBCFCDD8E1CAFF492BFCF0488E6B8C
3D08D416284E9C9C4FF36F474C9D46F3601652D5
512789C90D76785C061A88A0B92F5F5778E80BAA
735C8A382400C985B85D27C67369EF4E7ED30135
798755794D124D00EAB65653442957614400D71D
4F52A4A5BA897F055393174B3DFCA1D022416B88
8EDFE9667ECFE469BF88A5A5EBBB9A75334A48B9
5B45731C6BBA7359770D99124183E8D80548B64F
C0F8C75110123BEE7DB5CA3503C3F5A50A1A055E
C8A514B0309BCDE73F7E28EB72EB6CB3ABE24FDD
AF1AE760F055120CA658D20A21E4B14244BC047D
A1C515B965FB0DED176A0F38C811E6423D9FFD86
B9067085701B206D2AC180E82D5BC68EDD584A8B
77625ADEA198F6756E5D7C613811A5864E9874EA
Sathurbot dll:
F3A265D4209F3E7E6013CA4524E02D19AAC951D9
0EA717E23D70040011BD8BD0BF1FFAAF071DA22C
2381686708174BC5DE2F04704491B331EE9D630B
2B942C57CEE7E2E984EE10F4173F472DB6C15256
2F4FAA5CB5703004CA68865D8D5DACBA35402DE4
4EBC55FDFB4A1DD22E7D329E6EF8C7F27E650B34
0EF3ECD8597CE799715233C8BA52D677E98ABDFD
0307BBAC69C54488C124235449675A0F4B0CCEFA
149518FB8DE56A34B1CA2D66731126CF197958C3
3809C52343A8F3A3597898C9106BA72DB7F6A3CB
4A69B1B1191C9E4BC465F72D76FE45C77A5CB4B0
5CCDB41A34ADA906635CE2EE1AB4615A1AFCB2F2
6C03F7A9F826BB3A75C3946E3EF75BFC19E14683
8DA0DC48AFB8D2D1E9F485029D1800173774C837
AC7D8140A8527B8F7EE6788C128AFF4CA92E82C2
E1286F8AE85EB8BD1B6BE4684E3C9E4B88D300DB
Additional payloads:
C439FC24CAFA3C8008FC01B6F4C39F6010CE32B6
ABA9578AB2588758AD34C3955C06CD2765BFDF68
DFB48B12823E23C52DAE03EE4F7B9B5C9E9FDF92
FAFF56D95F06FE4DA8ED433985FA2E91B94EE9AD
B728EB975CF7FDD484FCBCFFE1D75E4F668F842F
59189ABE0C6C73B66944795A2EF5A2884715772E
C6BDB2DC6A48136E208279587EFA6A9DD70A3FAA
BEAA3159DBE46172FC79E8732C00F286B120E720
5ED0DF92174B62002E6203801A58FE665EF17B76
70DFABA5F98B5EBC471896B792BBEF4DB4B07C53
10F92B962D76E938C154DC7CBD7DEFE97498AB1E
426F9542D0DDA1C0FF8D2F4CB0D74A1594967636
AA2176834BA49B6A9901013645C84C64478AA931
1C274E18A8CAD814E0094C63405D461E815D736A
61384C0F690036E808F5988B5F06FD2D07A87454
F32D42EF1E5ED221D478CFAA1A76BB2E9E93A0C1
594E098E9787EB8B7C13243D0EDF6812F34D0FBA
1AAFEBAA11424B65ED48C68CDEED88F34136B8DC
BA4F20D1C821B81BC324416324BA7605953D0605
E08C36B122C5E8E561A4DE733EBB8F6AE3172BF0
7748115AF04F9FD477041CB40B4C5048464CE43E
3065C1098B5C3FC15C783CDDE38A14DFA2E005E4
FA25E212F77A06C0B7A62C6B7C86643660B24DDA
FADADFFA8F5351794BC5DCABE301157A4A2EBBCF
B0692A03D79CD2EA7622D3A784A1711ADAABEE8D
9411991DCF1B4ED9002D9381083DE714866AEA00
Associated domains
DNS:
zeusgreekmaster.xyz
apollogreekmaster.xyz
C&C:
jhkabmasdjm2asdu7gjaysgddasd.xyz
boomboomboomway.xyz
mrslavelemmiwinkstwo.xyz
uromatalieslave.space
newforceddomainisherenow.club
justanotherforcedomain.xyz
artemisoslave.xyz
asxdq2saxadsdawdq2sasaddfsdfsf4ssfuckk.xyz
kjaskdhkaudhsnkq3uhaksjndkud3asds.xyz
badaboommail.xyz
Torrent trackers:
badaboomsharetracker.xyz
webdatasourcetraffic.xyz
sharetorrentsonlinetracker.xyz
webtrafficsuccess.xyz
Registry values
You may need to use a third-party tool, as Windows Regedit might not even show these:
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\SharedAccess\Parameters\FirewallPolicy\FirewallRules\{variable GUID} = “v2.10|Action=Allow|Active=TRUE|Dir=In|Profile=Private|Profile=Public|App=C:\\Windows\\explorer.exe|Name=Windows Explorer|”
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\SharedAccess\Parameters\FirewallPolicy\FirewallRules\{variable GUID} = “v2.10|Action=Allow|Active=TRUE|Dir=In|Profile=Private|Profile=Public|App=C:\\Windows\\system32\\rundll32.exe|Name=Windows host process (Rundll32)|”
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\ShellIconOverlayIdentifiers\0TheftProtectionDll = {GUID1}
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Classes\CLSID\{GUID1} = “Windows Theft Protection”
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Classes\CLSID\{GUID1}\InprocServer32 = “C:\\ProgramData\\Microsoft\\Performance\\TheftProtection\\TheftProtection.dll”
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Classes\CLSID\{GUID1}\InprocServer32\ThreadingModel = “Apartment”
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Classes\CLSID\{GUID2}
The {GUID2} entries are variable across samples and have 6 char long subkeys, content is binary type and encrypted – used to store variables, temporary values and settings, IP’s, C&C’s, UID
e.g. {GUID2} entries look like
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Classes\CLSID\{8E577F7E-03C2-47D1-B4C0-BCE085F78F66}\00000003
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Classes\CLSID\{8E577F7E-03C2-47D1-B4C0-BCE085F78F66}\00000002
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Classes\CLSID\{8E577F7E-03C2-47D1-B4C0-BCE085F78F66}\00000001
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Classes\CLSID\{8E577F7E-03C2-47D1-B4C0-BCE085F78F66}\00000009
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Classes\CLSID\{8E577F7E-03C2-47D1-B4C0-BCE085F78F66}\00000011
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Classes\CLSID\{8E577F7E-03C2-47D1-B4C0-BCE085F78F66}\00010001
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Classes\CLSID\{8E577F7E-03C2-47D1-B4C0-BCE085F78F66}\00010002
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Classes\CLSID\{8E577F7E-03C2-47D1-B4C0-BCE085F78F66}\00000008
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Classes\CLSID\{8E577F7E-03C2-47D1-B4C0-BCE085F78F66}\00000007
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Classes\CLSID\{8E577F7E-03C2-47D1-B4C0-BCE085F78F66}\00000004
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Classes\CLSID\{8E577F7E-03C2-47D1-B4C0-BCE085F78F66}\00000010
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Classes\CLSID\{8E577F7E-03C2-47D1-B4C0-BCE085F78F66}\00020001




