Little by little, smartphone users are beginning to understand how important it is to protect their devices so malware can’t be installed on them. As the information stored on our phones becomes increasingly sensitive, the risk of losing it becomes increasingly real, and the consequences of such a loss become disproportionately more significant.
However, many users are unaware of what measures they can take to identify malicious activity on their devices. To complicate the picture, when the attacker gets to the final link in the chain of steps that make up a mobile attack, and the threat is finally installed on the victim’s device, they may take certain measures to prevent the threat from being noticed.
Delaying the malicious action, using only Wi-Fi networks, or reducing the level of activity when the user is operating the device are some of the strategies used by the malware to conceal itself. Nonetheless, eventually the malicious activity will have to kick into action, and that’s when you can pay attention to certain signs to detect illegitimate activity.
Signs that may indicate a mobile infection: Has your phone been compromised?
#1: You notice the system or apps behaving strangely
One possible clue to diagnosing malware on the device is the sudden failure of apps that usually work fine. If you haven’t updated the system or the app in question recently, and then unexpectedly that app suddenly starts closing or displaying various error messages, it may be that some malicious code on your device is interfering with its normal running processes.
The malware may try to take advantage of vulnerabilities present in the system’s apps, using them to access permissions that have been granted to them, or to violate the platform and run commands with administrator permissions. Such attempts to exploit the weaknesses of other apps may result in errors that can be noticed by the user.
Additionally, a malicious app may overuse the device’s resources. Given that smartphones and tablets are personal devices that we get to know in great detail, you may notice that the device isn’t functioning as usual: calls and messages don’t reach their destination, you run out of battery more quickly than usual, etc.
Being aware beforehand of what apps are installed on your phone will make it easier to identify any app that you didn’t authorize. Taking a look at the permissions used by this app will enable you to see whether it could be creating charges in your name through online purchases.
You need to bear in mind that many malicious apps disguise themselves as system components, so an app may be something other than what it appears to be. If the app has requested administrator permissions, you may not be able to uninstall it through the system settings. For this reason, it’s important to be extremely careful with what permissions you grant to apps when they are installing—or running.
#2: Your call or message history includes some unknown entries
Regularly checking your call history for unknown numbers is an excellent habit to adopt. Lots of malware families try to make calls or send messages to premium international numbers. Such malware ends up having a direct impact on the user, who unjustly has to pay the costs.
Our products identify this type of malware under the Android/TrojanSMS family. If we analyze the number of new variants of this family that have been created since the start of this year, we can see the extent of this family’s growth. On average, about 50 new examples are detected each month. Unfortunately, this trend shows no sign of decreasing in the near future.
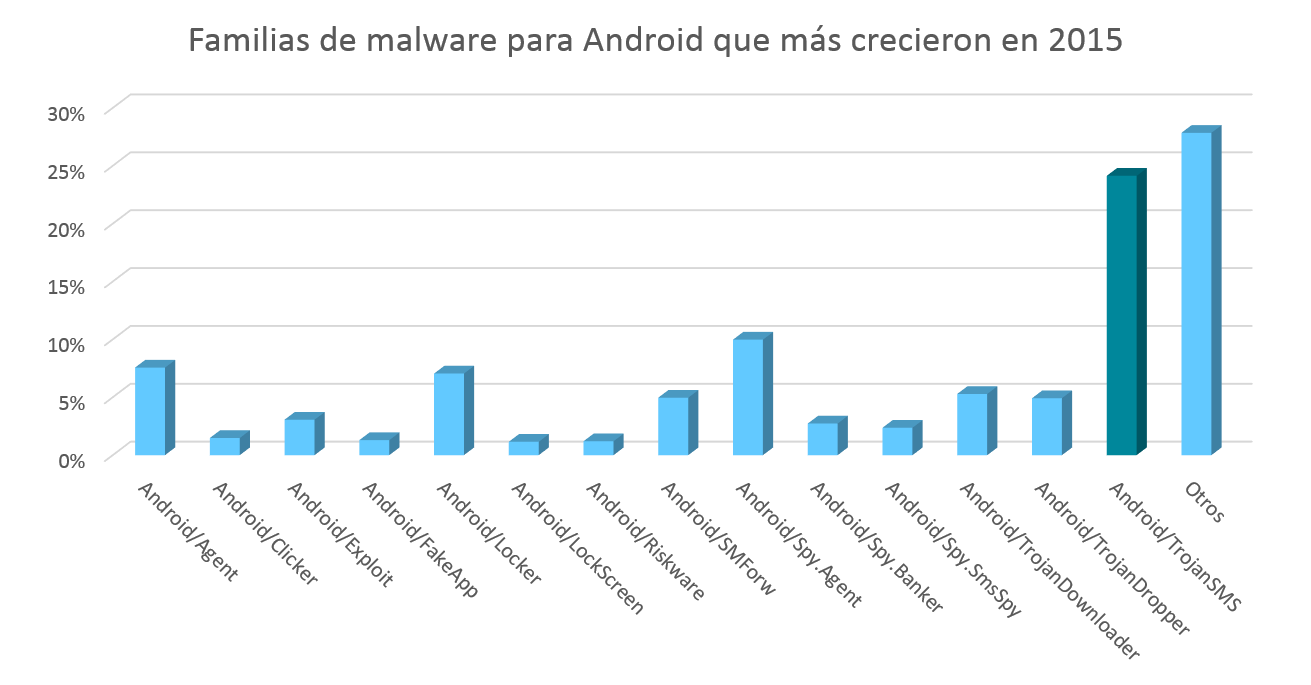
| Familias de malware para Android que más crecieron en 2015 | Families of malware for Android that grew most in 2015 |
| Otros | Others |
#3: Excessive data usage
Malicious apps may be using the data system to communicate with command and control centers operated by cybercriminals in order to download orders and updates, as well as send back information stolen from the device.
If you usually check how much data your apps use, you will quickly become aware of any changes to the normal pattern. Below you can see a screenshot that shows a description of data usage by an Android app. This way, you can check the times when the sending and receipt of data is highest and compare this with your use of the device. If there is an excessive amount of data exchange taking place at times when you don’t use the device, you have grounds for suspecting that something strange is going on.
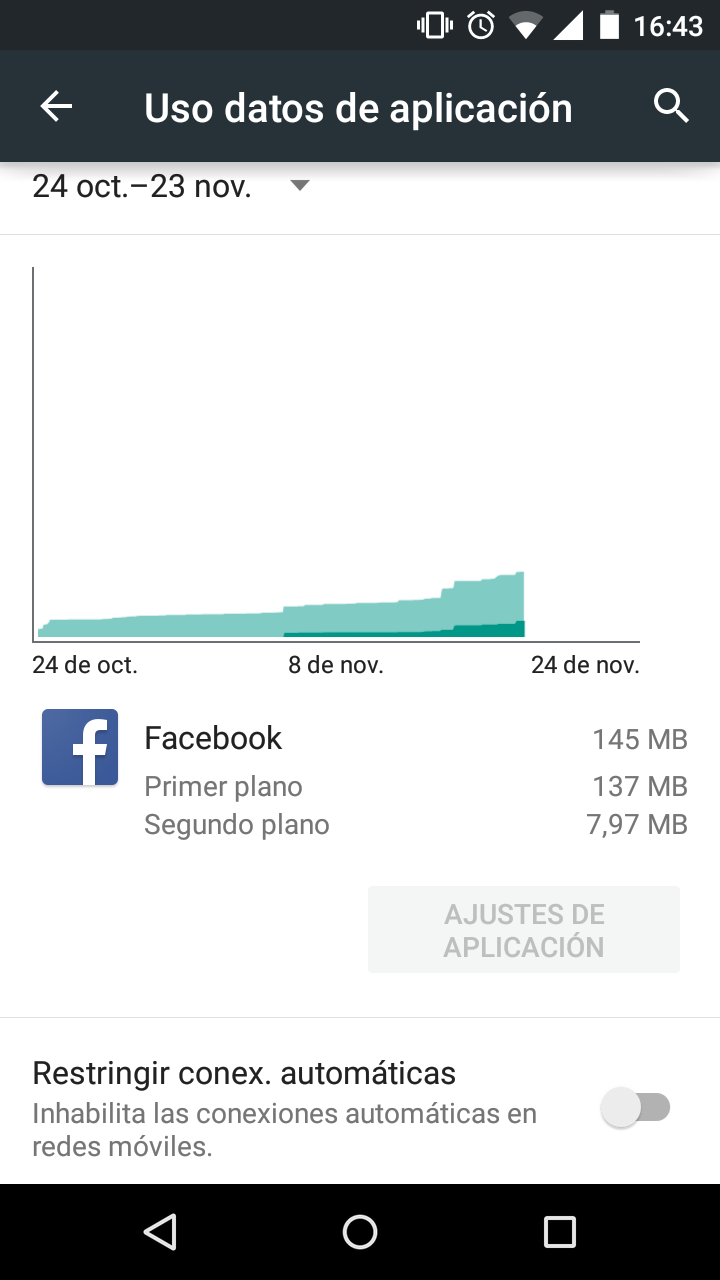
| Uso datos de aplicación | App data usage |
| 24 oct.-23 nov. | Oct 24–Nov 23 |
| 24 de oct. | Oct 24 |
| 8 de nov. | Nov 8 |
| 24 de nov. | Nov 24 |
| Primer plano | Foreground |
| Segundo plano | Background |
| AJUSTES DE APLICACIÓN | APP SETTINGS |
| Restringir conex. automáticas | Restrict automatic connections |
| Inhabilita las conexiones automáticas en redes móviles. | Disable automatic connections on mobile networks. |
#4: You or your contacts receive strange text messages
One method used a lot by cybercriminals to control infected mobile devices is sending text messages containing commands to be interpreted by the malware, which then takes the corresponding action. Lots of examples of malware manipulate message logs to delete any such messages that could raise the user’s suspicions, but others don’t bother with such precautionary measures, in which case the user can read the content that is received and sent.
For example, the following image illustrates the “conversation” held between an emulator infected by a bot and the machine that acts as the control center. In this case, the user would be able to notice that text messages were being received, containing the order “ping”.
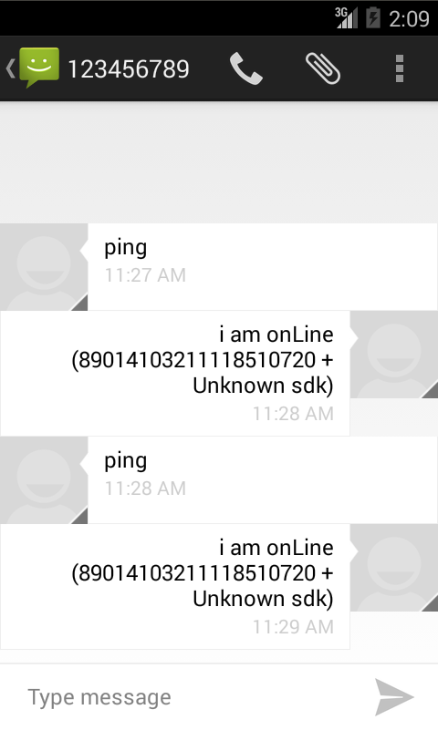
Mobile malware can also send text messages to phone numbers from the user’s list of contacts as a way to propagate itself, using this method to get the recipients to download malicious content via specific links. If your friends receive strange messages from your phone, you should check what apps are installed on it.
#5: Your payment breakdown includes actions you did not make
Sending text messages, making calls, and using the data system will result in increased costs, which the user will be responsible for. Examining the costs attributed to your mobile phone number on a monthly basis is a good practice to be able to detect any malicious activity quickly.
You also need to take into account the fact that a lot of malware tries to pass through official app stores to steal your credit card data. For this reason, if you regularly make such payments through your mobile device—or any other platform—you should also check the transactions through such services to ensure there are no unwarranted charges.
What steps should you take if your phone has been compromised or infected?
If for any of the reasons mentioned above you believe you may have been infected by malware, you can install a trustworthy security solution to scan your device in order to identify the threat. You can also contact the official customer services provided by the seller so they can look into the problem.
If you have the technical know-how, you can try to remove the threat yourself through a command console.
Furthermore, if you suspect that sensitive information stored on your device may have been stolen, you can change your credentials for accessing any services you have used on your device.
Prevention is better than cure
To avoid any unpleasant experiences when using your device and be able to enjoy the available technology safely, you should take a proactive and preventive approach to keep the data on your mobile device secure:
- Always keep your device’s operating system and apps updated with the latest available versions.
- Make a backup copy of all data on the device, or at least the most important data.
- Use security solutions provided by a highly reputable company and keep them up to date.
- Be sure to use only official stores for downloading apps, where the likelihood of becoming infected by malware is lower—although still not zero.
- Use a screen lock, and remember thatthe pattern may be easy to guess and less secure than a PIN, and that a password is your best option.
- Encrypt the content on your device.
- Try to avoid running rootingor jailbreaking processes on the device.




